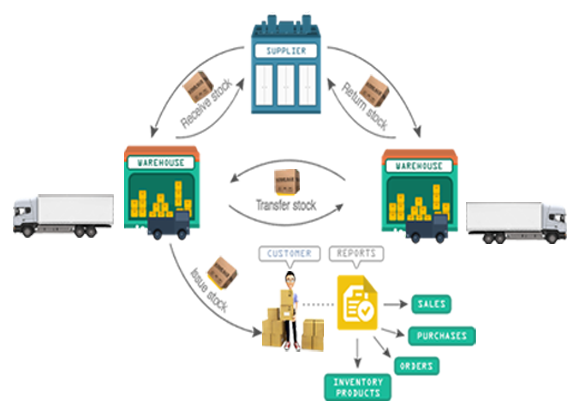
Warehouse management systems (WMS) are best described as the advanced technology
and operating processes that optimize all warehousing functions. These functions
typically begin with receipts from suppliers and end with shipments to customers,
and include all inventory movements and information flows in between.
Warehouse management systems have typically been associated with larger, more
complex distribution operations. Small, non-complex distribution facilities have
historically not been viewed as candidates to significantly streamline operations
and reduce costs.
However, even smaller and midsize companies are increasingly recognizing the
significance of warehouse management systems in today's environment of integrated
logistics, just-in-time delivery, and e-commerce fulfillment.
In practice, successful WMS solutions are generally designed to merge computer
hardware, software, and peripheral equipment with improved operating practices for
managing inventory, space, labor, and capital equipment in warehouses and distribution centers.
Implementation of a WMS allows a company to increase its competitive advantage by
reducing labor costs, improving customer service, increasing inventory accuracy, and
improving flexibility and responsiveness. A WMS enables a company to manage inventory
in real time, with information as current as the most recent order, shipment, or receipt
and any movement in between.